Logging protections rescinded from national forests

Logging protections rescinded from national forests pose significant risks to ecosystems and community welfare, increasing concerns about wildlife habitat loss, water quality degradation, and the long-term sustainability of forestry practices.
Logging protections rescinded from national forests has sparked conversations about balancing ecological preservation and resource management. What does this mean for our forests?
Impacts of rescinding logging protections
Understanding the impacts of rescinding logging protections is essential for grasping the broader implications for our forests and the environment. When these protections are lifted, it can open the door to increased logging activities, which can potentially alter ecosystems significantly.
Environmental Changes
One of the most concerning outcomes is the change in biodiversity. Areas that were once safe from logging may now face threats to wildlife habitats.
Economic Impacts
Additionally, while logging can create short-term economic benefits, such as job creation, the long-term economic repercussions may include degraded forest health, leading to higher costs for restoration. When we log unsustainably, we risk depleting resources needed for future generations.
- Loss of wildlife habitat
- Alteration of water cycles
- Soil erosion and degradation
Another effect is the potential for increased soil erosion. Trees play a critical role in anchoring the soil in place. With fewer trees, the risk of erosion rises, which can impact water quality in nearby streams and rivers.
Community Responses
Local communities often respond with concerns over their way of life, especially if their livelihoods depend on the forest. Without the protective measures in place, many fear the consequences of uncontrolled logging.
Understanding these impacts is crucial. By recognizing the balance that needs to be maintained between logging and protection, we can engage in more informed discussions regarding our forests’ future.
Environmental concerns related to logging

The environmental concerns related to logging are numerous and serious. As we continue to explore the implications of reduced protections, it becomes clear that the health of our forests is at stake. Logging can drastically change landscapes, affecting not just the trees but the entire ecosystem.
Biodiversity and Habitat Loss
One of the major issues is the loss of biodiversity. When trees are cut down, many species lose their natural habitats. This can lead to the decline of various plants and animals, some of which may be endangered.
Water Quality and Soil Erosion
Another significant concern is water quality. Forests play a crucial role in filtering pollutants and maintaining clean water. Without trees, there may be more runoff, leading to increased sediment in rivers and lakes. This runoff can harm aquatic life as well.
- Reduced carbon storage
- Increased greenhouse gas emissions
- Disruption of local climates
Logging can also contribute to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, and cutting them down releases this greenhouse gas back into the atmosphere. This can exacerbate climate change, which poses additional risks to our environment.
Impact on Local Communities
The effects of logging extend to local communities as well. People who rely on forests for their livelihoods may find their resources diminished. As logging encroaches on protected areas, traditional land uses can be threatened.
Understanding these environmental concerns is vital for shaping future policies. By recognizing the delicate balance of our ecosystems, we can better advocate for sustainable practices that protect both our forests and the communities that depend on them.
Sustainable forestry practices
Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems while allowing for the use of forest resources. These practices enable us to meet our needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. Through responsible management, we can ensure that our forests continue to thrive.
What Are Sustainable Practices?
Sustainable forestry focuses on methods that protect the biodiversity of forests while promoting economic viability. This includes selective logging, which allows some trees to remain standing. Such practices help maintain habitats for wildlife.
Benefits of Sustainable Forestry
Implementing sustainable practices can provide various benefits, including:
- Improved forest health
- Economic stability for local communities
- Enhanced wildlife habitats
Healthy forests improve air and water quality. When we practice sustainable forestry, we also contribute to climate change mitigation. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, which is crucial in combating global warming.
Community Involvement
Involving local communities in forestry management is vital. When communities have a stake in the process, they are more likely to support sustainable practices. Education about the importance of forests helps encourage responsible use and conservation efforts.
By embracing sustainable forestry practices, we can strike a balance between our needs and the health of the environment. This approach supports both current and future generations, ensuring that we maintain the beauty and vitality of our forests.
Community reactions to policy changes
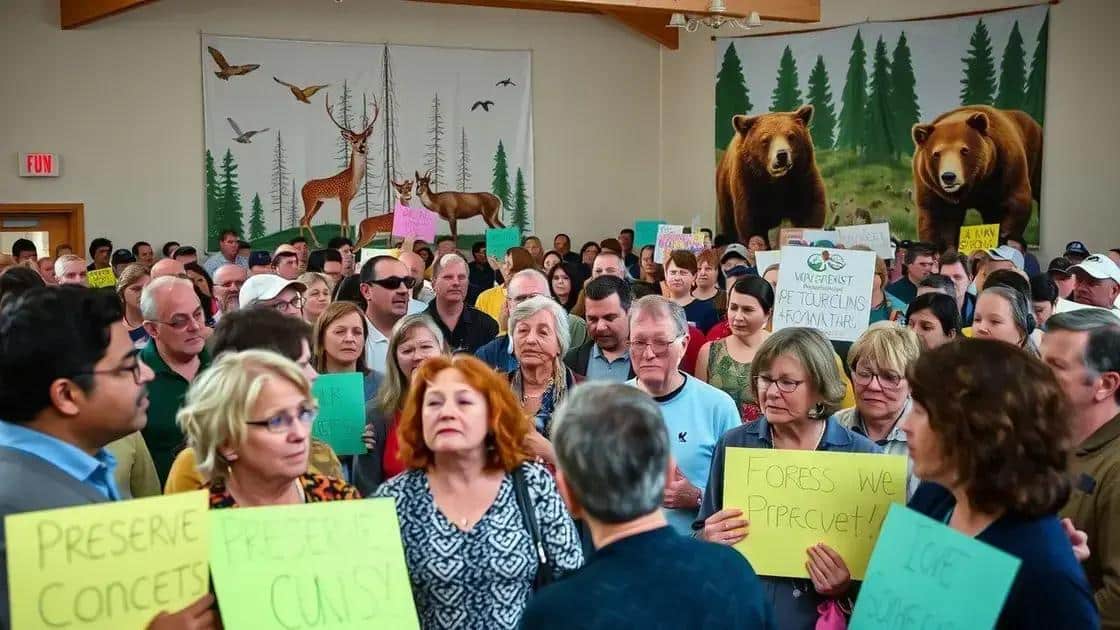
Community reactions to policy changes regarding logging protections can vary widely. As individuals hear about these changes, many express their concerns about the potential impacts on their lives and local environments. The lifting of protections often raises alarms about the future of local forests and wildlife.
Public Concerns
Many community members worry about the direct effects on their livelihoods. For instance, those involved in eco-tourism may fear that logging will diminish the beauty of natural landscapes, which attracts visitors. Communities that rely on the forest for resources often find themselves in a difficult position.
Advocacy and Mobilization
In response to policy changes, communities tend to mobilize quickly. Advocacy groups often emerge to protect local ecosystems. These groups may hold meetings, rallies, and social media campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of maintaining forest protections.
- Concerns over wildlife habitats
- Effects on air and water quality
- Economic implications for local businesses
People frequently voice their concerns about the effects of logging on local wildlife. The fear of losing species and natural habitats fuels public interest. Additionally, many realize that logging can lead to decreased air and water quality, raising further alarm among residents.
Local Government Involvement
Local governments play a crucial role in addressing community fears. Town halls and public forums provide a platform for residents to voice their opinions. Proactive engagement by officials can help ease tensions and foster dialogue about sustainable practices.
The reactions of communities to these policy changes highlight the vital connection between people and their environment. By understanding the concerns of residents, policymakers can create more balanced solutions that consider both economic needs and environmental protection.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Logging Protections and Community Impact
What are logging protections?
Logging protections are regulations that limit or restrict logging activities to preserve ecosystems and protect wildlife habitats.
Why are communities concerned about rescinding logging protections?
Communities worry that lifting protections could harm local wildlife, decrease air and water quality, and negatively impact their livelihoods.
How can communities engage with policy changes?
They can participate in town hall meetings, join advocacy groups, and voice their concerns to local government officials to influence decisions.
What are sustainable forestry practices?
Sustainable forestry practices aim to manage forest resources responsibly, ensuring that ecosystems remain healthy while meeting economic needs.





